Your cart is currently empty!
What is meant by ‘Site-Specific’ antibody labeling?
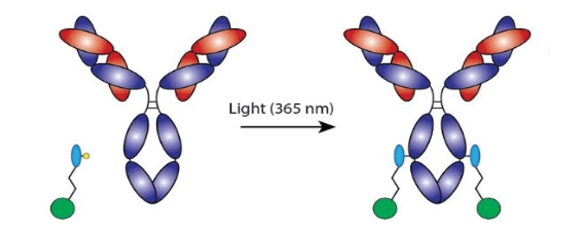
Site-specific labeling refers to the precise placement of a label (e.g. oligonucleotide, drug, epitope tag, biotin, fluorescent dye, click chemistry group, enzyme, etc.) onto a protein or antibody. In the case of the oYo-Link® antibody labeling system, antibodies are site-specifically labeled on the constant region (i.e. Fc region). Since antibodies are symmetric, oYo-Link results in up to two labels per antibody.
Site-specific labeling ensures uniform labeling of up to 2 labels per Antibody on the heavy chain.
The Problem: Heterogeneous/Non-Specific Labeling Hurts Antibody Performance
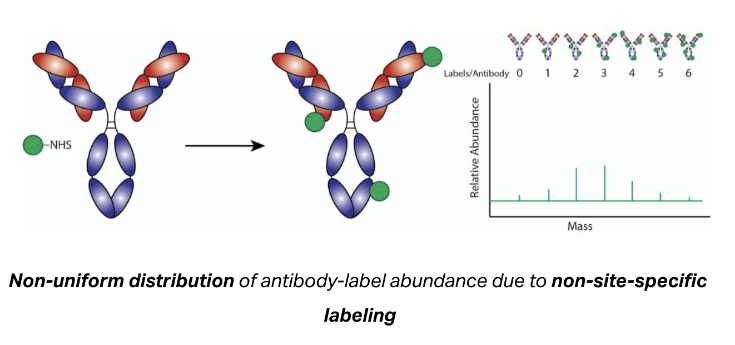
Typically, any antibody labeling reagent that does not explicitly indicate site-specific labeling will label the antibody via its lysine residues. Since antibodies have many lysines and a variable number and location of lysines from antibody to antibody, the extent of labeling is very heterogeneous. The labels can reside anywhere on the antibody, including within the antigen-binding site. This can negatively impact antibody binding & decrease assay performance.
Effective Binding & Uniform Surface Immobilization
Site-specific antibody labeling ensures that the label does not interfere with antigen binding. This becomes particularly important when attaching large biomolecules to the antibody (e.g. enzymes), which can sterically prevent antigen binding.
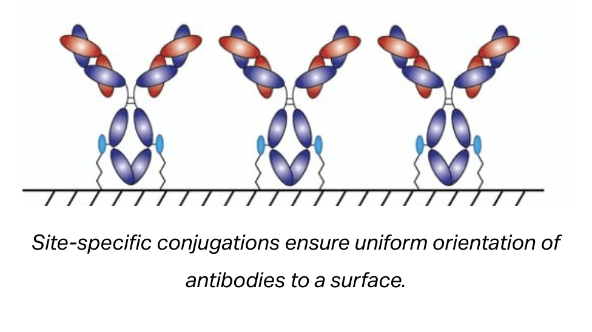
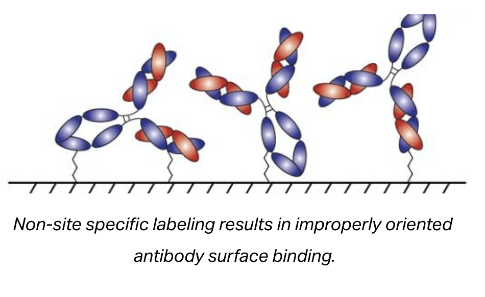
Site-specific labeling also ensures the proper orientation of immobilized antibodies. Proper orientation of antibodies on surfaces can result in a significant improvement in the density of available antigen binding sites on the surface and in turn improve the sensitivity of most immunoassays.
Compatibility with Antibodies & Buffers
The oYo-Link® site-specific antibody labeling system avoids the need to optimize reaction conditions for each antibody. The same reaction conditions are used for all oYo-Link compatible antibodies and results in a predictable number of labels per antibody. In contrast, the efficiency of non-site-specific labeling of lysines can vary dramatically from antibody to antibody. As a result, the reaction conditions may need to be optimized to achieve the desired results.
A particularly notable advantage of the oYo-Link site-specific antibody labeling system is that antibody labeling can be conducted in nearly any buffer, including those containing amines (e.g. Tris) or storage proteins (see Buffer Compatibility Table). In contrast, reagents that rely on lysine labeling typically require the removal of storage proteins and/or exchange of amine-containing buffers. This is not only time-consuming, but can result in a significant loss of antibody.
oYo-Link® vs Competitor Antibody Labeling Reagents & Kits
| Feature | oYo-Link® | Other Antibody Labeling Reagents |
|---|---|---|
| Labeling technology | Site-specific | Random |
| Antibody concentration requirement | >50ug/mL | 1mg/mL |
| Buffer requirements | Almost no limit | No Tris, No BSA, No Glycerol etc |
| Stabality of regeants | Highly stable | Loss of activity after reconstitution |
| Single/multiple use | Multiple use | Single use |
| Stability of conjugated antibody | Highly Stable | May cause aggregation |
| Antibody binding affinity | Maintained | Lowered or lost |
| Verification of antibody conjugation | Run on SDS-PAGE gel | Hard to know |
| Removal of free reagents | No need in most applications | Removal required |
Why use oYo-Link® over other site-specific labeling systems?
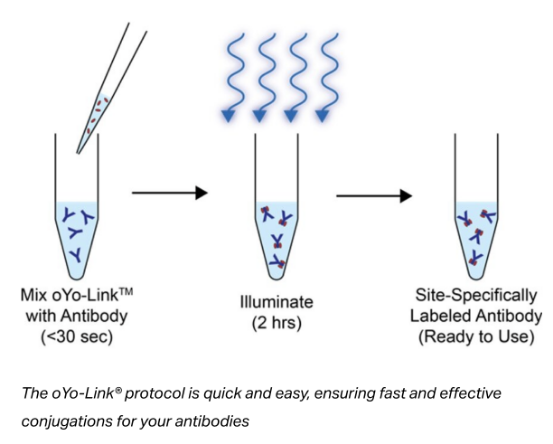
oYo-Link® is Simple, Fast, and Site-Specific.
The entire procedure requires just two-steps and less than than 30 seconds of hands-on time. The reaction is complete in just 2 hours.
Compare this with other site-specific labeling methods that require the use of multiple enzymes, hours of hands on time, and as much as a day to acquire a final product.
Covalent, Site-Specific Labeling to Avoid Dissociation
While some other site-specific methods may claim to be rapid, these generally do not result in a covalent linkage between the label and the antibody. Therefore, the label can dissociate from your antibody during your experiment. This can result in loss of signal, increased background, or both.
Our Products

oYo-Link® SureLight® PE-Cy7
Exc/Emm: 488 nm / 572 nm, 776 nm
Rapid, site-specific labeling of compatible antibodies with up to two PE-Cy7 labels. 30 seconds hands-on time, conjugates ready in just 2 hours.

oYo-Link® SureLight® Far Red APC
Exc/Emm: 713nm/718nm
Rapid, site-specific labeling of compatible antibodies with up to two Far Red APC labels. 30 seconds hands-on time, conjugates ready in just 2 hours.
oYo-Link® HRP
Applicable for direct conjugation of HRP to primary antibodies for ELISA, IHC & western blotting.
oYo-Link® Oligo Custom
Label as little as 1 µg of Antibody with your custom oligo per reaction. Oligos made by IDT. Supports ssDNA and dsDNA up to 80bp or longer in length.
Citations & Resources for Learning more about Site-Specific Conjugations:
Siler Panowski, Sunil Bhakta, Helga Raab, Paul Polakis & Jagath R Junutula (2014) Site-specific antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy, mAbs, 6:1, 34-45, DOI: 10.4161/mabs.27022
Zhou Q. Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation for ADC and Beyond. Biomedicines. 2017;5(4):64. Published 2017 Nov 9. DOI:10.3390/biomedicines5040064
Christopher R Behrens & Bin Liu (2014) Methods for site-specific drug conjugation to antibodies, mAbs, 6:1, 46-53, DOI: 10.4161/mabs.26632
Makaraviciute A, Ramanaviciene A. Site-directed antibody immobilization techniques for immunosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;50:460-471. DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.06.060
Site-Specific Antibody–Drug Conjugates: The Nexus of Bioorthogonal Chemistry, Protein Engineering, and Drug Development Paresh Agarwal and Carolyn R. Bertozzi Bioconjugate Chemistry 2015 26 (2), 176-192 DOI: 10.1021/bc5004982
Meldal M, Schoffelen S. Recent advances in covalent, site-specific protein immobilization. F1000Res. 2016;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-2303. Published 2016 Sep 12. DOI:10.12688/f1000research.9002.1